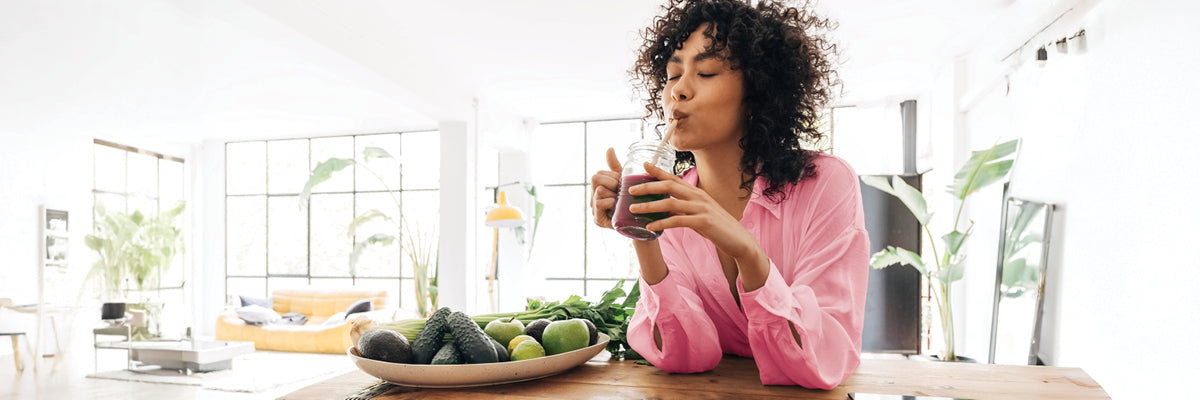
This unique prenatal multivitamin is a clean, allergen-free, vegan formula specifically developed to meet the essential nutrient needs of expectant mothers and their babies’ health trajectory.*
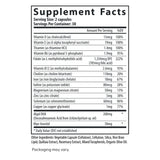
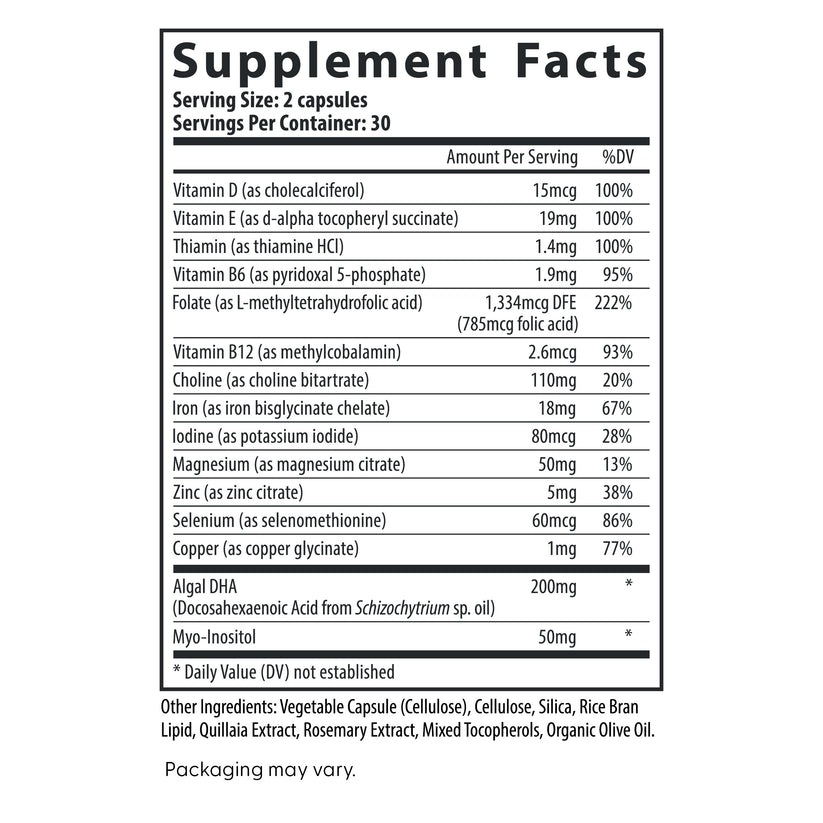
Prenatal Multivitamin Essentials with DHA is specially formulated with selected nutrients that support the baby’s growth and development, including healthy brain, nervous system, bone, and eye health development.* Plus, each dose provides 15 essential nutrients using bioavailable and bioactive, or methylated, forms of vitamins at levels that fill gaps in a mother’s diet and support a healthy pregnancy, including the following:
- Choline plays a crucial role in fetal brain and central nervous system development, aiding in cognitive benefits for the baby.(1-3)
- Adequate intake of DHA during pregnancy has been associated from long-term outcome studies with various benefits for the baby, including improved cognitive development, better vision, and reduced risk of certain developmental disorders.(4)
- Myo-inositol supports balanced glucose metabolism for the mother, which is helpful for healthy gestational term, development, and birth weights.(5,6)
- Adequate folate in healthful diets may reduce a woman's risk of having a child with a brain or spinal cord birth defect.(1-3)
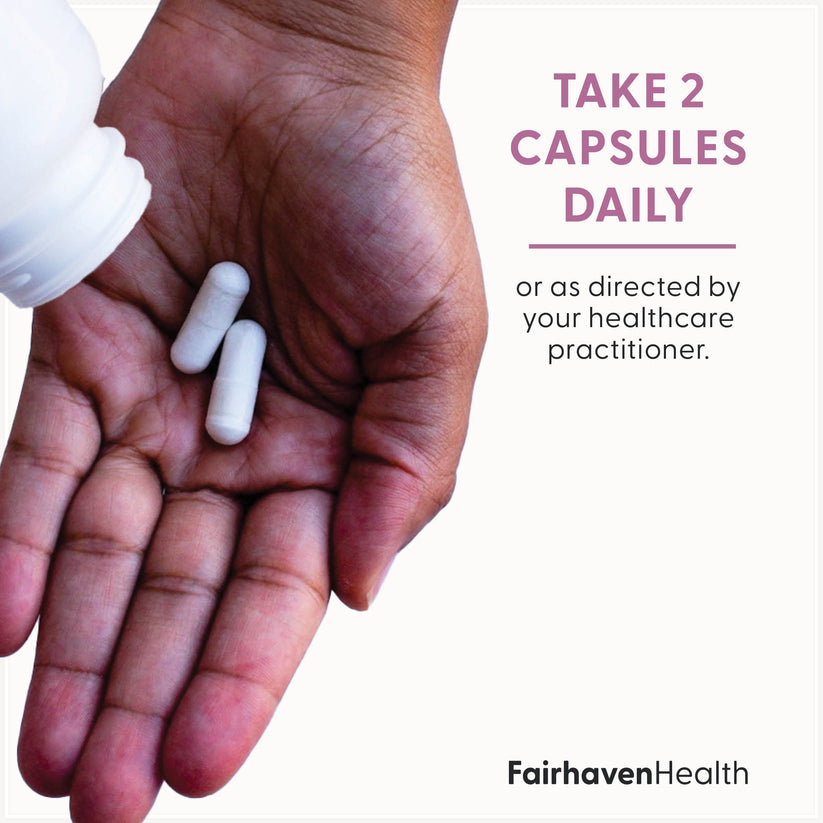
Prenatal Multivitamin Essentials with DHA is available in a small, convenient, easy-to-swallow capsule, enhanced with an antinausea aromatic scent to alleviate the nausea associated with morning sickness.
Clean, Vegetarian Formulation
Prenatal Multivitamin Essentials with DHA is made without gluten, dairy, yeast, soy, artificial colors, or preservatives. It’s manufactured in the USA using domestic and imported ingredients in a GMP-registered manufacturing facility.
Packaging and label may vary.
References
1. Schwarzenberg S et al. Pediatrics. 2018;141(2):e20173716.
2. Derbyshire E et al. Nutrients. 2020;12(6):1731.
3. Trujillo-Gonzalez I et al. FASEB J. 2019;33(8):9194-9209.
4. Mun J et al. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):1125.
5. Vitale SG et al. Intl J Endocrinol. 2016(8085):1-9.
6. Zheng X et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(42):e1604.